For a devops engineer, load balancing is a popular word. You need to figure out a way to scale the system so that it can manage it correctly when enormous traffic enters your system. One alternative is to boost the running single node’s efficiency. Adding more nodes and distributing the job among these nodes is another option. Having many nodes has another high availability added benefit.
Envoy proxy is a proxy service that in the growing trend has been used as a service mesh. In this blog post, we’ll see the load balancing aspect of the Envoy Proxy.
Load Balancers
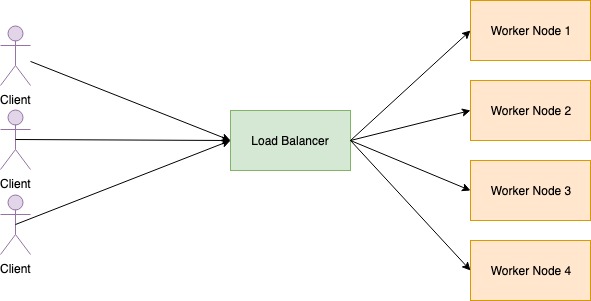
Load balancers is an endpoint that listens to the request that comes into the computation cluster. When application enters the Load Balancer, it checks for accessible worker nodes and distributes requests among worker nodes. Load balancer has the following characteristics.
- Service Discovery: Check available worker nodes
- Health check: Regularly inspect worker nodes health.
- Load balancing: Distribute the request between the worker nodes.
Proxy
Proxy is an intermediate element that exists between two endpoints. Proxy service will take requests from the client and forward them to the target server. There are two kinds of proxies. Forward proxy and reverse proxy. Instead of sending application straight to the endpoint, we can also send it via a proxy. This proxy type known as the Forward proxy. Forward proxy frequently used to bypass firewall constraints and access blocked websites.
Revers proxy is a form of proxy service that takes incoming client requests and transmits them to the server that can satisfy them. The outcome will be routing back to the client. In addition, proxy also provides more control over the client request. It can also cache the application and speed up the efficiency of the network. Reverse Proxy used to
- To enable indirect access when a website disallows direct connections as a security measure.
- To stream internal content to Internet users.
- To allow for load balancing between severs.
- To disable access to a site.
Load balancing topologies
Proxy standing between client endpoint and backend endpoint. Load balancing can be split into following topologies depending on where proxy service is positioned.
Middle Proxy
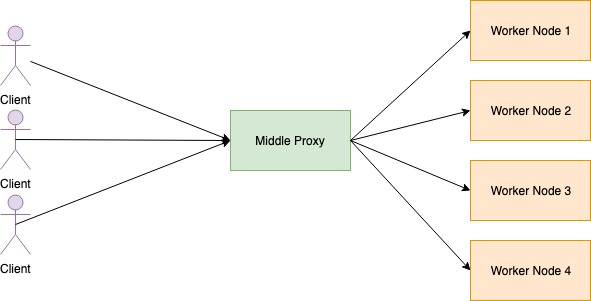
All request from the client goes into the middle proxy. Middle proxy rout request into the worker nodes. This sort of load balancers is easy and straight forward.
Embedded Client Library
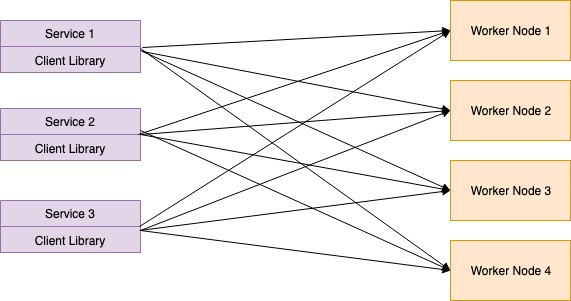
The largest issue in the Middle Proxy is the single point failure. If the Middle Proxy server gets down, then client services are unable to access backend facilities. In this form of proxy, load balancing is performed by the client itself instead of main load balancing. Using gRPC libraries, this type of mechanism can be introduced.
In this sort of load balancers, growing complexity becomes an issue. Developers also need to install load balancing components for each service.
Side Car Proxy
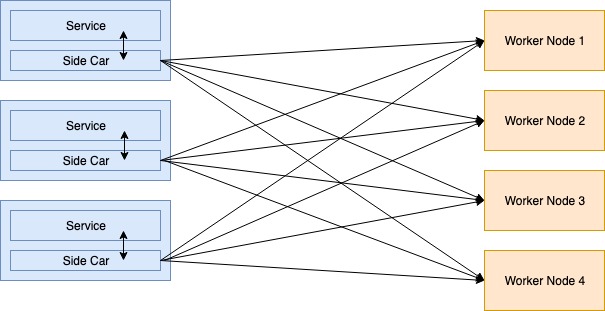
The biggest issue in the Embedded Client Library is the complexity of constructing communication element for each of the services. Client Library divided into the containers with the latest trend of using container technology. There is no lock in programming languages while designing decentralized load balancers. This is known as a side car. This type of application of the proxy service known as Service Mesh. Side Car responsible for routing customer requests into the suitable backend service.
Envoy is a high quality reverse proxy published by Lyft in C++ language. Envoy used in Service Mesh to interconnect services. The following are common terminology used by Envoy Proxy.
- Host: An entity capable of network communication.
- Downstream: Hosts that send request to the envoy proxy.
- Upstream: Host that receive request from the envoy proxy.
- Listener: Named network location that can connect to an envoy proxy through a downstream.
- Cluster: Cluster is group of logically same upstream host that envoy can connect. Envoy can discover cluster by using service discovery.
Front Envoy Proxy
Aport from Side Car Proxy, Envoy can also be configured as a Front Proxy. Front proxy configured as the main load balancer to the request from the public internet. This proxy also know as edge proxy. Service Mesh’s overall architecture would be as follows.
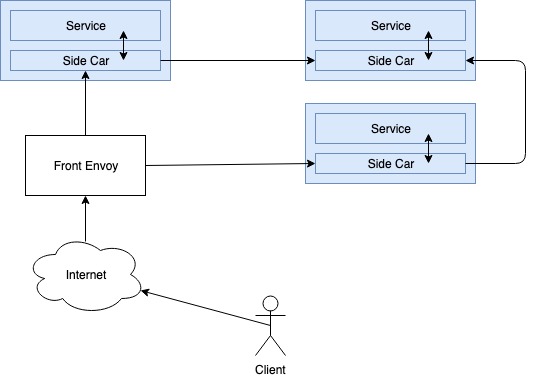
Here, the front proxy has been used as a load balancer for incoming Internet traffic. Also conduct termination of TLS here. Then request routing via side car proxies to the appropriate facilities. Service mesh can identify services that are accessible through service discovery. It also provides circuit brake characteristics for handling failure overs. Collectively, Envoy provides a whole lot of characteristics to implement a Service Mesh.
Types of Load Balancers in Envoy Proxy
When proxy need to acquire connection to host in upstream cluster, the cluster manager use following polices to rout traffic.
-
Round Robbin Rout load to each of the worker nodes(upstream host) circular order. All worker node consider as same and all node get same amount of load.
-
Random Select worker node by random and rout the traffic. This is know to be perform better than Round Robbin policy.
-
Weighted Least Request This policy based on the number of connection that are keep while loading balance. Assume there are two worker nodes with same specs. Due to some reason first worker node take longer time to response. So it also have to keep it connection to first worker node longer than second node. In this scenario, load balancer can put more weight on second worker node rather sending traffic into the first node.
-
Original Destination This type of load balancer used when a given connection needs to connect to some particular upstream host. host selected by reading client’s meta data.
Other than load balancing, Envoy also provide following feature to implement Service Mesh.
- Dynamic service discovery
- TLS termination
- HTTP/2 and gRPC proxies
- Circuit breakers
- Health checks
- Staged rollouts with %-based traffic split
- Fault injection
- Rich metrics
We will go through each of these features in next article. This article is to give you the basic introduction about Envoy Proxy and how it do Load Balancing. See you in another article. Cheers :)
References

 Draw image on Github contribution graph
Draw image on Github contribution graph