The database is the heart of handling data in a software application. Unless it is not an in-memory database, the database stores data on the disk as a file. Your application may be running on a remote server, and the database also resides on a remote server. Your application may collect sensitive data such as passwords, bank account data, health data, etc. The databases that persist data in a disk use a file to store data of a database. Imagine a hacker login into your database server and stolen your database file. Now, unfortunately, a hacker is able to access all of your information by reading that file. So, how could you overcome this problem?
Hide Data With Encryption
Encryption is commonly used in day-to-day network communication to hide data from the third party. Encryption scrambles your data by a given key. Only the person who knows the right key can read the real message. Encryption could be either symmetric or asymmetric. In this case, we just need symmetric encryption since the user does not need to generate a shared secret.
The simplest solution to overcome this problem is by storing data encrypted rather storing as a flat file. But, encrypting the whole file is not a practical solution since its need to decrypt the whole database file to execute each of the SQL queries. It is a huge performance drawback. Instead of encrypting the whole file, we can use pages to encrypt database data as blocks. Pages are the smallest unit of transaction in a database. Pages are fixed in size (normally 4KB). Pages used to store Btree nodes in a database — these nodes can be either a collection of table rows or keys that used for indexing (to learn more about Btree and Pages, read this blog post)
How Transparent Data Encryption Works
Now, keeping data on a remote file is not an issue since now we know we can store data in an encrypted form. Here on, we are going to discussing how everything fits in together. For that, let us see how MySQL implements this feature.

Here, an application needs to store a table in MySQL server. It sends SQL query to the MySQL server. MySQL server read the database pages to evaluate the SQL expression. But, Page is in the encrypted format. Now, the database needs to find the relevant key to decrypt page. Obviously, you need to keep this key in a secure place. Key Vault is a secure vault that is used to store such keys, certificates, and passwords. MySQL read the key from Key Vault and decrypt the pages and execute the SQL Query. If any modification happens on Pages, then it encrypts the page and saves it on the file. Here, AES encryption is used with CBC mode used to encrypt and decrypt the data.
Key Vault Architecture
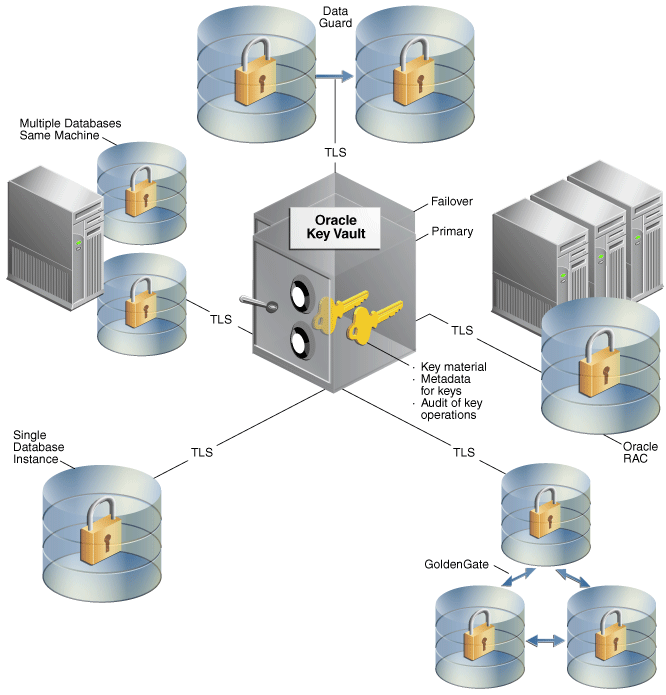
Key vault provides centralized storage to store keys even in the distributed database. Instead of using separate keys for multiple TDE requirements, you can maintain a single key called the master key. Additional to storing keys, key vault provides a way to administrate roles. The following are the roles used in the Oracle Key Vault.
- System Administrator
- Key Administrator
- Audit Manager
The system administrator has the authority to create, modify, and delete a user. It can add a new endpoint to the system. Further, this role is responsible for scheduling backup and setting up high availability.
The key administrator controls user and endpoint access to the virtual wallet. It can manage user groups and endpoint groups.
Audit manager has read access to all security objects. It is responsible to manage the audit trails.
Pros and Cons
It seems like TDE is a nice way to save data from a hacker. However, TDE has both pros and cons when using in the production.
Pros
- Easy to implement
- No changes required in the application layer
- Features such as Mirroring, Always On, and Log Shipping can be used along with TDE
Cons
- Data secured only when it is at rest. The database server still can read your data and keys.
- Data not required to hide is also stored in encrypted form.
- Small performance impact due to encryption overhead.
- The database backup may become heavier when compressed
Other Database Encryption Methods
Other than using TDE to hide data in page level, Column Level encryption also available. In this case, the database encrypts the column rather encrypting pages. This makes column level encryption much more flexible compared to TDE. Further, Databases can use separate keys to encrypt each of the columns. Performance of the database becomes a drawback since multiple keys used to encrypt a single database.
Conclusion
TDE protect your data in remote database server by using encryption. Purpose of the TDE is secure data in databases file level (at rest). Almost all of the commercial databases provide the ability to use TDE to protect data. Even though you use TDE to secure your database from a hacker, still you need to take action to save your data from other possible adversaries such as XSS attack, SQL injection, Replay attack, etc. Designing software that runs on the web requires a lot more security than it runs as a single desktop application. Therefore, the whole design should be tightly secure in order to provide a fully secure platform for the end user.

 How Database B-tree Indexing works
How Database B-tree Indexing works